
#Mutex vs semaphor software#
Both the software and hardware solutions are present for handling critical section problems. Process synchronization plays an important role in maintaining the consistency of shared data. It prevents problems like a race condition.As per operating system terminology, mutex and semaphores are kernel resources that provide synchronization services, also called synchronization primitives. A semaphore is used for signalling the availability of resources. It will get access to the desired resource when the mutex is unlocked.īoth mutex and semaphores are important utilities needed for managing the different processes within an operating system. It has to wait until the count of the semaphore is larger than 0.īut in case of a mutex, if it is locked, the process has to wait.
#Mutex vs semaphor free#
If no resource is free then the process needing a resource executes wait operation. On the other hand, a mutex is actually a variable. Only the process that has acquired a lock can release the lock on the mutex. Whereas, in case of a mutex, it is modified only by the process that may request or release a resource. The processes obtaining or releasing a lock can have ownership on the semaphore value.

The wait and signal operations can modify a semaphore. But, the mutex is a locking mechanism used for handling processes. Semaphore vs Mutex Basic differenceĪ semaphore is a signalling mechanism used during process synchronization. If the processes occupy the resources, the semaphore value becomes 0. After releasing the resource, the signal is executed. Here the wait () operation is executed when a resource is necessary. According to the number of resources in the system, this value is initialised. For implementing mutual exclusion, this type of semaphore can be used.Ĭounting semaphore – This type of semaphore can handle more than one resource. After releasing the resource, the value is incremented by 1. The signal operation is executed when if the process releases a resource. Then the value of the semaphore changes from 1 to 0. Here, when a process requires a resource, it executes the wait operation. The two types of semaphores are as follows:īinary semaphore – In this semaphore, the value ranges between 0 and 1. This is done when there are no processes blocked in the queue. Signal () – This method controls the exit of a thread from the critical section. There can be a situation where the value of S is negative. This is only done when the value of Wait is positive.
The method only decreases the value of the argument S. Wait () – This method controls the entry of a thread inside the critical section. The two methods of modifying the semaphore are as follows: During this time, other processes cannot alter it. Suppose a process is modifying the value of a semaphore. The variable is modified by two functions – signal and wait. What is Semaphore?Ī semaphore is a variable that is very important for process synchronization. The coder has to unlock it as many times it was locked. This determines the number of times it was locked or unlocked. This is possible in case of a recursive mutex.

However, you can lock a mutex more than once. This is a condition where multiple resources try to access the same point of time. The thread will only get access to the resource after the lock is released. In this case, the process is put on hold in a queue. The other process may want to obtain the lock on the mutex object. The other threads that have to use the resource follow the same process. After using the resource, the thread releases the lock on the mutex. Suppose the program thread has to utilise the resource, the lock on the mutex object is occupied. This mutex object is then created with a unique ID or name. When a program initialises, a mutex object is created for a resource. They are not allowed access simultaneously. But these resources can do it only at a particular point in time.
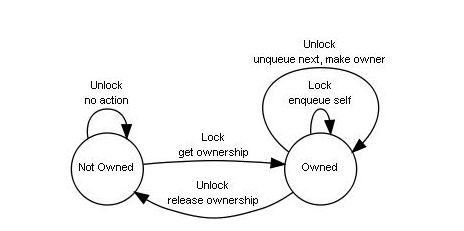
In an operating system, a Mutex is used for protecting the critical section.Ī mutex will allow many threads to access a single resource. The process cannot enter the critical section when another process is present. Mutual exclusion is a condition where only a process can access the resource at a given time. The resource access is operated by a mutex. Mutex actually stands for Mutual Exclusion Object. In this article, we will take a look at their basic differences to get a better understanding of them. A semaphore is used as a signalling mechanism. Mutex is basically a locking method for a resource. The most popular of these methods is Mutex and Semaphore. The critical section problem can be solved using software methods. Along with this, the critical section problem can be handled. By proper process, synchronization data inconsistency can be avoided. Here system resources are shared and concurrent access is provided for this data. In any operating system, process synchronization is extremely important for sharing data in a way that it remains consistent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
